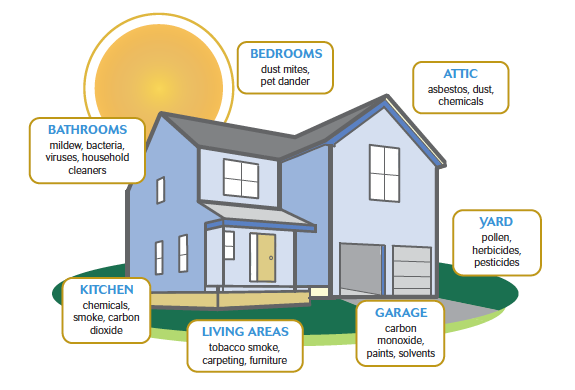
With modern lifestyles, it is no surprise that indoor air pollutants are becoming an increasingly pervasive problem. The sources of these contaminants can vary from dust and mold to pet dander and other allergens, as well as combustion byproducts such as carbon monoxide or radon.
This article will discuss the most common types of indoor air pollutants, their health risks, and the steps you can take to reduce exposure. We’ll also provide tips on how to detect and remedy any presence of indoor air pollutants. Let’s get started.
Common Indoor Air Pollutants And Solutions
Indoor air quality can be affected by a variety of pollutants, such as:
1. Dust
Dust is the most common source of indoor air pollution and can present a risk for allergies, asthma, and other respiratory issues. Dust consists of tiny particles such as pet dander, mold spores, dust mites, and other particles that accumulate inside. Also, household dust can contain heavy metals, such as lead. To reduce dust levels, it is important to vacuum regularly and clean areas that accumulate dust. Also, using a damp cloth to clean and an air filter can help reduce dust levels in the home.
2. Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an odorless, colorless, and poisonous gas found in many combustion sources, such as unvented kerosene space heaters, wood stoves, fireplaces, and gasoline engines. Carbon monoxide can cause serious health problems, even death, if not detected in time. To reduce carbon monoxide levels, it is important to ensure that all combustion sources are properly vented to the outside and regularly inspected and maintained. Additionally, installing a CO detector can help alert you of unsafe gas levels.
3. Volatile Organic Compounds
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are chemicals released into the air from products or materials such as paints, glues, air fresheners, and cleaning supplies. VOCs can cause various health issues, including eye irritation, headaches, asthma attacks, and cancer. To reduce VOC levels, it is important to read product labels carefully and use products with low VOC ratings. Additionally, adequate ventilation can help disperse VOCs from the air.
4. Radon
Radon is a colorless and odorless gas found naturally in many soils. It can enter homes through cracks in the foundation, pipes, and other openings. Radon can cause many health issues and is the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers. To reduce radon levels in the home, it is important to test for radon and use proper mitigation techniques if necessary. Additionally, sealing cracks in the foundation and around windows and doors can help prevent radon from entering the home.
5. Secondhand Smoke
Secondhand smoke is a mixture of the smoke that comes from the burning end of tobacco products, such as cigarettes and cigars, and the smoke exhaled by people smoking. It can cause various health issues, including asthma attacks, bronchitis, respiratory infections, and cancer. To reduce secondhand smoke levels in your home, it is important to ensure no smoking occurs inside. Furthermore, increasing ventilation can help reduce smoke levels in the home.
6. Pet Dander
For many people, pets are an important part of their lives. However, pet dander can be a source of indoor air pollution. Pet dander is small particles of skin and hair shed by animals that can cause asthma attacks and other allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Also, pet dander can accumulate on floors, bedding, and furniture. To reduce pet dander levels in the home, it is important to vacuum regularly and use air filters. Keeping pets outside bedrooms and other living areas to reduce allergen levels.
7. Mold
Mold is a fungus that can grow on damp surfaces and in areas with high humidity. It can cause health problems like respiratory illness, asthma attacks, and allergic reactions. Also, mold may cause structural damage to your building or home if it is left unchecked. Keep humidity below 50 percent to limit mold growth and promptly fix any leaks or standing water.
Consider using a dehumidifier in areas that are prone to dampness or moisture. Clean up any existing mold with detergents, bleach, and other disinfectants. Inspect for mold and address any potential issues immediately and regularly.
8. Asbestos
Asbestos is a fibrous material commonly used in building materials until the late 1970s. It can cause serious respiratory problems if inhaled over time. To identify whether asbestos is present in your home or building, you should hire a qualified professional to inspect. If asbestos is found in materials that are likely to become airborne, they should be sealed or removed by a certified asbestos removal contractor. Regularly inspect for new cracks or signs of damage and contact a professional immediately if any are found.
9. Pesticides
Pesticides control pests such as insects, rodents, and weeds. While they may effectively control pests, they can also cause health problems when inhaled or ingested. To reduce pesticide exposure in the home, use organic pest control methods whenever possible. If you must use chemical pesticides, ensure proper ventilation and avoid using them indoors.
10. Lead
Lead is a naturally occurring metal found in rocks and soil. However, it can also enter your indoor environment through the air. It has been known to cause serious health issues such as learning problems, behavioral difficulties, and brain and nervous system damage. As with other indoor air pollutants, lead exposure is particularly dangerous for children because their bodies are still developing.
To minimize your family’s exposure to lead, replace any painted surfaces made before 1978 and use a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter to remove dust particles from carpets and furniture. Furthermore, you may consider having your home tested for lead if it was built before 1980.
Following these guidelines can help improve indoor air quality and protect your health and the health of those around you. Regularly monitoring the air quality in your home or building is a good way to ensure that pollutants are kept at safe levels and reduce household air pollution exposure.
Indoor Air Pollution And Health
Air pollution doesn’t just come from outside air sources. Household activities and products, mold, pets, and other contaminants can also pollute indoor air. These pollutants can cause long-term and short-term health problems for the people in your home.
1. Immediate Effects
The most common immediate effects of indoor air pollution are irritation to the eyes, nose, and throat. This is due to pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and other allergens, which can cause coughing, sneezing, and respiratory problems. Also, short-term exposure to high levels of pollutants can cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, and fatigue.
2. Chronic Effects
Long-term exposure to indoor air pollution can be even more serious than the immediate effects. Allergies, asthma attacks, and other respiratory problems may not show up until months or years after initial exposure. Prolonged exposure to certain pollutants can lead to more serious health concerns such as cancer, heart disease, or neurological disorders.
Also, children, the elderly, and people with pre-existing conditions or weakened immune systems are particularly susceptible to the effects of indoor and outdoor air pollution. They should be monitored closely if they live in a home with high levels of air pollution.

How Safe Is Your Air?
After understanding the common sources of indoor air pollutants, it is important to ask: How safe is my air? The answer depends on the type of pollutant, its concentration, and your exposure time. Some pollutants are generally not considered dangerous at low levels, while others can cause serious health problems when their concentrations exceed certain thresholds.
Different people may experience different levels of sensitivity to indoor air pollutants. This could be due to age, health status, and lifestyle habits. For example, children and the elderly are more vulnerable to certain types of pollution. Also, people with asthma or allergies are more likely to have irritated eyes, noses, and lungs due to certain indoor pollutants.
It is important to regularly monitor the air quality in your home, office, and other indoor spaces. This can be done by using air quality monitors that measure the levels of different air contaminants inside a room. If you find that the readings are elevated, you can take action to reduce the levels of pollutants. This could include improving ventilation and using air filters to capture certain particles.
Air Quality Index (AQI)
The AQI is an index that evaluates air quality inside and outside the home. It can help you measure and monitor air pollution levels in your household, so you can take steps to improve it if necessary. The index considers several pollutants, such as ozone, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter. AQI levels are based on a scale from 0 to 500, with higher numbers indicating that air pollution is unhealthy for anyone exposed.
If you’re worried about indoor air pollutants in your home, it’s important to get an accurate reading of the AQI inside your house as well as outside. You can do this by using an air quality monitor to indicate the current AQI levels in your home. If you find that the AQI is higher than it should be, then you can take steps to improve it.
Tips To Deal With Poor Indoor Air Quality
If you are concerned about indoor air quality problems, there are some steps you can take to improve them.
1. Increase Ventilation
Ensure fresh air is circulating throughout the home by opening windows and doors and running exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens. It is also important to check ventilation systems and insulate air ducts, such as heating and cooling ducts, and look for blockages or obstructions. Also, look into energy-efficient ventilation systems that can help circulate fresh air while keeping your home at a comfortable temperature.
2. Clean Regularly
Dust, dirt, and other pollutants can collect in carpets and furniture, so regular cleaning is essential to maintain good indoor air quality. Vacuum carpets regularly and use damp cloths to dust furniture and other surfaces. It is also important to wash bedding frequently, as dust mites and other allergens can accumulate in mattresses and duvets.
3. Avoid Pollutants
Minimizing the use of products carrying indoor air pollutants, such as air fresheners and aerosols, can help reduce household air pollution. Smoking indoors should also be avoided, as second-hand smoke can cause many health issues. Also, avoid using toxic products, such as paints and solvents, around the home.
4. Use Natural Air Purifiers
Some plants are excellent at improving air quality by absorbing pollutants from the atmosphere. Spider plants, Areca palms, and rubber trees are some of the best for removing toxins from indoor air. Place them throughout your home to create a healthier environment.
5. Maintain Humidity Levels
Keeping relative humidity levels between 30 and 50 percent is important for maintaining good indoor air quality. Increasing ventilation, using dehumidifiers, and running exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens can help reduce humidity levels if they are too high.
These steps can help ensure your home is free from air pollutants and enhance your overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Indoor air pollutants can seriously affect human health and well-being, from the long-term effects of environmental hazards to the immediate impacts of irritants. People must take steps to identify potential sources of indoor air pollution and develop strategies to mitigate any threats posed by them.
From understanding common airborne contaminants to taking preventive measures to reduce the impact of indoor air pollutants, it is important to be aware of your home’s air quality to keep you and your family safe. With the right knowledge and precautionary steps, indoor air pollution can be prevented or minimized.


